Semaglutide, a medication initially developed for managing type 2 diabetes, has gained widespread attention for its weight loss benefits. As more individuals seek effective solutions for weight management, semaglutide has emerged as a leading option, providing substantial results in clinical trials and real-world applications. In this article, we delve deep into the dosage guidelines, the science behind its efficacy, and essential considerations for those looking to use semaglutide for weight loss.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It mimics the GLP-1 hormone, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, reducing appetite, and slowing gastric emptying. While it was initially approved for treating type 2 diabetes under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus, its remarkable weight loss effects have led to its approval for obesity treatment under the brand name Wegovy.
How Semaglutide Aids in Weight Loss
The mechanism of action for semaglutide involves several physiological processes that contribute to weight loss. By stimulating GLP-1 receptors in the brain, semaglutide helps reduce hunger and increase satiety, leading to lower calorie intake. Additionally, by slowing down the rate at which food leaves the stomach, semaglutide prolongs the feeling of fullness after meals. This dual-action approach makes it easier for individuals to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet, resulting in significant weight loss over time.
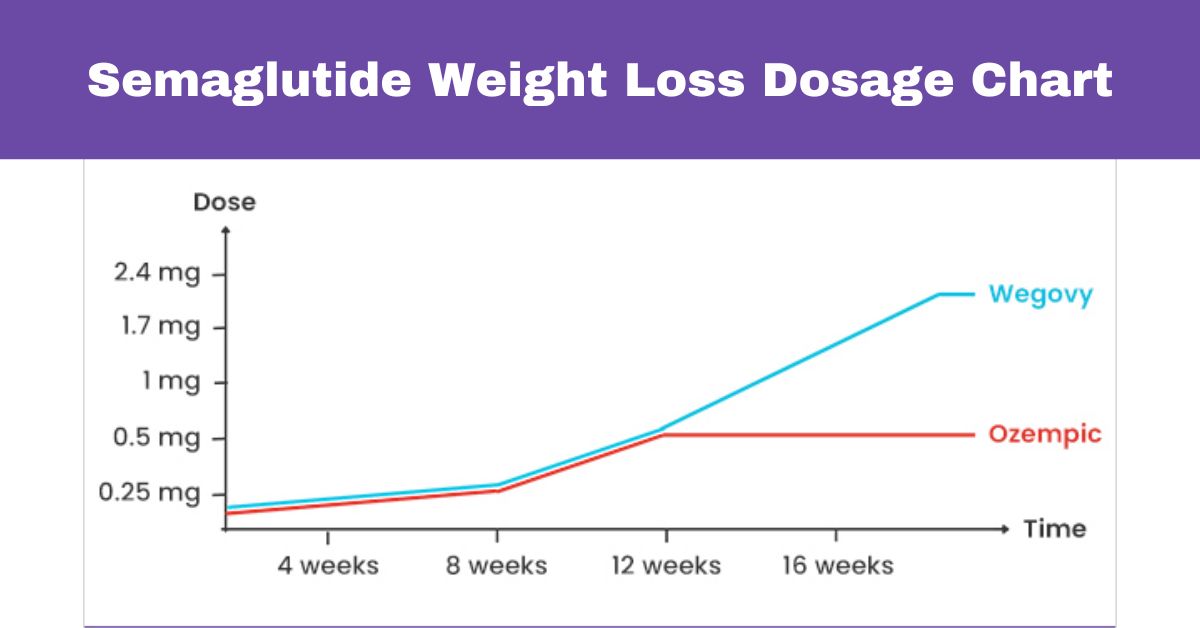
Recommended Dosage for Weight Loss
Initial Dose
For individuals beginning semaglutide for weight loss, the starting dose is typically 0.25 mg once weekly. This lower dose is crucial for minimizing potential side effects, such as nausea, which is common when starting GLP-1 receptor agonists. The 0.25 mg dose is maintained for four weeks, allowing the body to adjust to the medication.
Titration Phase
After the initial four weeks, the dose is gradually increased to enhance the medication’s effectiveness. The titration schedule is as follows:
- Weeks 5-8: Increase the dose to 0.5 mg once weekly.
- Weeks 9-12: If well-tolerated, the dose is further increased to 1.0 mg once weekly.
- Weeks 13-16: The dose is then increased to 1.7 mg once weekly.
- Week 17 onwards: The maintenance dose of 2.4 mg once weekly is reached.
This gradual increase is designed to optimize weight loss while managing side effects.
Maintenance Dose
The maintenance dose of semaglutide for weight loss is 2.4 mg once weekly. This dosage is sustained to ensure continued appetite suppression and weight loss. Studies have shown that this dose can lead to an average weight loss of 15-20% of initial body weight over a 68-week period, making it one of the most effective pharmacological options for weight management.
Administration Guidelines
Semaglutide is administered via a subcutaneous injection. The injection can be self-administered into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. It’s crucial to rotate injection sites to prevent skin irritation. The medication should be taken on the same day each week, at any time of the day, with or without meals.
Tips for Reducing Side Effects
While semaglutide is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or headaches. To minimize these side effects, consider the following:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Eat smaller meals: Opt for smaller, more frequent meals to reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Avoid high-fat foods: These can exacerbate nausea.
If side effects persist, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss potential adjustments to your dosage or administration schedule.
Who Should Consider Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
Semaglutide is recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, or those with a BMI of 27 or greater who have at least one weight-related condition, such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia. It’s important to note that semaglutide should be used as part of a comprehensive weight management program, including a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before starting semaglutide, it’s essential to consider certain precautions:
- History of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC): Individuals with a personal or family history of MTC should avoid semaglutide.
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2): This genetic condition also contraindicates the use of semaglutide.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Semaglutide is not recommended for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to potential risks to the fetus or infant.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Treatment
Regular monitoring is essential for individuals on semaglutide to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Healthcare providers typically recommend:
- Regular weight check-ins: Monthly weight measurements to track progress.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as semaglutide can significantly lower blood sugar levels.
- Kidney function tests: Since GLP-1 receptor agonists can affect renal function, periodic kidney function tests are advised.
If weight loss plateaus or significant side effects occur, a healthcare provider may adjust the dosage or explore alternative weight management strategies.
Long-Term Benefits of Semaglutide
Beyond weight loss, semaglutide offers several long-term health benefits. These include improved cardiovascular health, reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and enhanced quality of life. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can reduce their risk of developing obesity-related conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Conclusion
Semaglutide represents a promising option for those struggling with weight management. By following the recommended dosage chart and working closely with a healthcare provider, individuals can achieve significant and sustainable weight loss. As with any medication, it’s essential to consider the potential risks and benefits, and to use semaglutide as part of a comprehensive approach to health and wellness.



